The Philippine Flying Lemur – Colugo
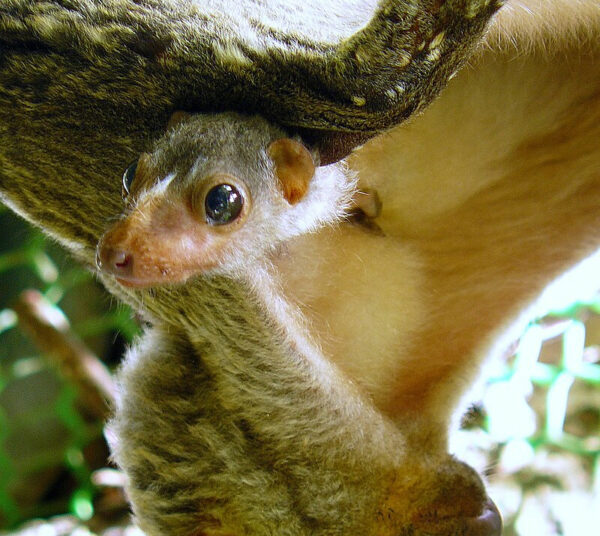

The Philippine Flying Lemur, known locally as colugo, is a fascinating creature that embodies the rich biodiversity of the Philippines. Despite its name, it’s neither a lemur nor a true flying animal; rather, it’s a gliding mammal with remarkable adaptations for life in the treetops. In this blog, we’ll delve into the characteristics, habitat, behavior and conservation status of this intriguing animal.
What is the Philippine Flying Lemur?
The Philippine Flying Lemur (Cynocephalus volans) is one of the two species of colugos, which belong to the order Dermoptera. They are unique to Southeast Asia and are most commonly found in the forests of the Philippines, particularly on the islands of Luzon, Mindanao, and Palawan.
Physical Characteristics
Colugos are often described as “flying lemurs” due to their gliding abilities, but they possess distinctive features that set them apart. They have:
Large Eyes – Adapted for nocturnal life, these large eyes help them see in low light conditions.
Membranous Patagium – A flap of skin stretches between their limbs, tail, and body, allowing them to glide gracefully from tree to tree. This membrane can span over a meter, making it possible for them to glide distances of up to 100 meters (about 328 feet).
Flat, Bat-like Face – Their facial structure, with a flattened nose, gives them a unique appearance.
Habitat and Distribution
Philippine Flying Lemurs thrive in tropical and subtropical forests, favoring primary and secondary growth areas. They are primarily arboreal, spending most of their time in the canopy, where they can easily glide and forage for food. These habitats are crucial not only for their survival but also for maintaining the overall health of the forest ecosystem.
Behavior and Diet
Colugos are nocturnal creatures, spending their days resting in the hollows of trees or clinging to branches. When night falls, they emerge to feed on a diet primarily consisting of leaves, fruits, and flowers. Their specialized digestive system allows them to extract nutrients from tough plant material, which most other animals would find difficult to digest.
Gliding Adaptations
Their gliding ability is a remarkable adaptation for escaping predators and moving efficiently between trees in search of food. By stretching their limbs and spreading their patagium, they can control their descent and glide smoothly, often changing direction mid-air to navigate around branches.
Conservation Status
The Philippine Flying Lemur is currently classified as Near Threatened by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN). Their populations are declining due to several factors:
Habitat Loss – Deforestation for agriculture, logging, and urban development poses a significant threat to their habitat.
Illegal Hunting – While not commonly hunted, they are occasionally captured for the pet trade or local consumption.
Climate Change – Changes in climate can impact their food sources and habitats.
Conservation Efforts
Efforts to protect the Philippine Flying Lemur include:
Habitat Protection – Establishing and enforcing protected areas to conserve their natural habitats.
Community Engagement – Working with local communities to promote sustainable land-use practices and raise awareness about the importance of biodiversity.
Research – Ongoing studies to better understand their ecology and behavior, which can inform conservation strategies.
The Philippine Flying Lemur is a remarkable example of the unique wildlife found in the Philippines. Its gliding abilities, distinct adaptations, and crucial role in the ecosystem make it a vital species deserving of our attention and protection. As we continue to face challenges related to habitat loss and climate change, supporting conservation efforts will be essential to ensure that future generations can marvel at this extraordinary creature.
If you ever find yourself in the lush forests of the Philippines, keep an eye out for this elusive glider, it’s a reminder of the incredible diversity that our planet holds!
References:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Philippine_flying_lemur